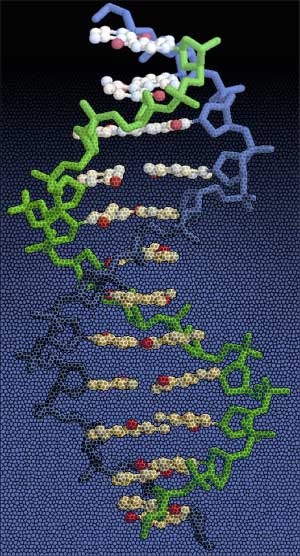
DNA
 Introduction Introduction
Deoxyribose nucleic acid, called DNA for short, is the biomolecule that is most responsible for providing a living organism with a way to store and express the information for life. It is also the medium by which genetic information is transferred from a parent to its offspring. Encoded upon the DNA strands are regions (also known as genes) with discrete instructions for producing the molecular tools required of all living organisms - namely proteins. The proteins that are produced have functional roles in just about every aspect of a living cell. Some proteins play a structural role in a cell. Other proteins are enzymes that regulate many biochemical pathways (anabolic and catabolic) in living organisms. The process of taking the genetic information and converting it to a protein, of which DNA plays an important role, is a fairly complicated process covered in greater detail in the discussion on ribonucleic acids (RNA). The basic chemistry of DNA is rather simple in comparison to the complex roles it plays.
|